Research column
Search: 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024
| 2024 | |
|---|---|
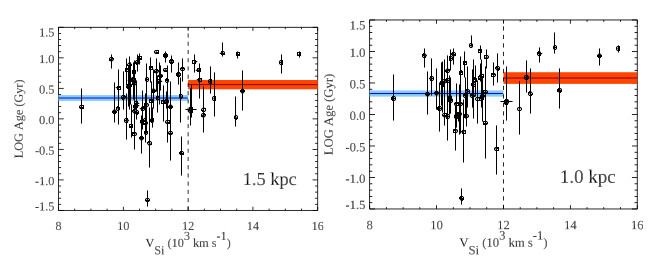 | The team led by Prof. Pan investigated the relation between SN Ia ejecta velocity and their host-galaxy environment, and found that there could exist a relationship between the two parameters. This study focused on the local environmental properties of SNe Ia and revealed possible trend that high-velocity SNe Ia tend to be associated with old stellar populations, while normal-velocity SNe Ia can be found in both old and young stellar populations. This result implies that the normal SNe Ia are likely produced by more than one channel, challenging the previous consensus that they are associated with a single and uniform population. This work has been published in
Lin & Pan et al., 2024, MNRAS, 531, 1988
|
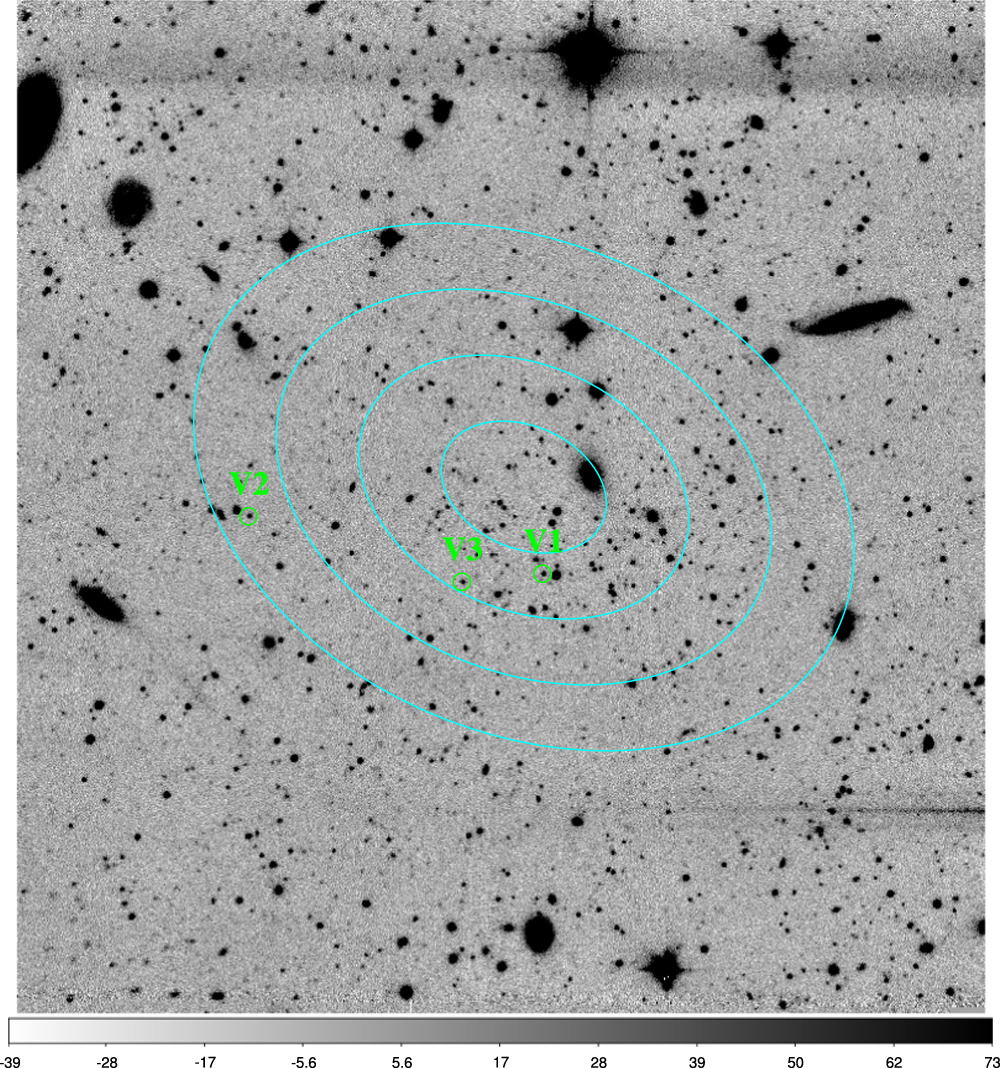 | Virgo III is a newly discovered ultra-faint dwarf (UFD) galaxy. We used the Lulin One-meter Telescope (LOT) to search for RR Lyrae associated with this UFD.With deep exposures of LOT that can reach to r~23 mag, we discovered three RR Lyrae, labeled as V1, V2, and V3 in this deep LOT images. Using the discovered RR Lyrae, we measured a distance of 154 kpc to Virgo III.
|
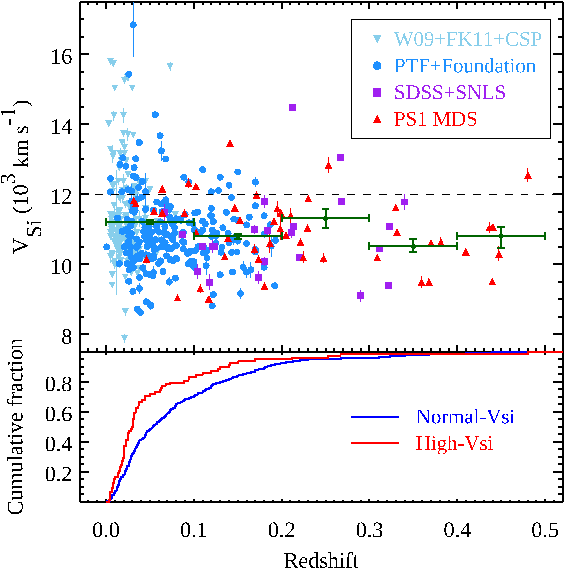 | An international team led by Prof. Pan studied the data obtained from Pan-STARRS1 Medium Deep Survey (PS1-MDS) and found the type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) could evolve with time. As one of the most mature cosmological probes, SNe Ia have homogeneous properties, and they were expected to be consistent and similar during the evolution of our Universe. However, this work suggests that SNe Ia are likely to have at least two different populations, as separated by their ejecta velocities. The fractions between different populations tend to evolve with time. This result could impact the precision of SNe Ia in probing the cosmic expansion and dark energy. This work has been published in
Pan et al., 2024, MNRAS, 532, 1887
.
|
