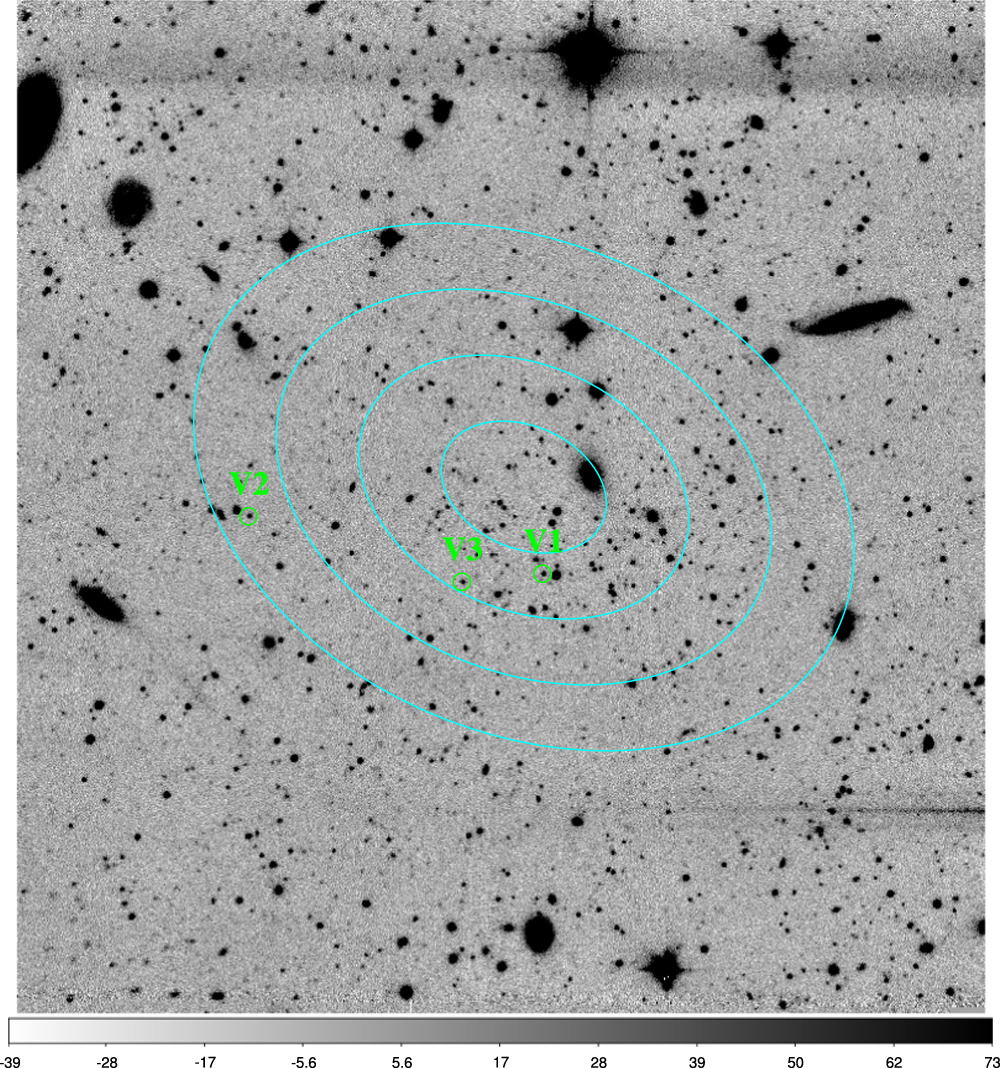
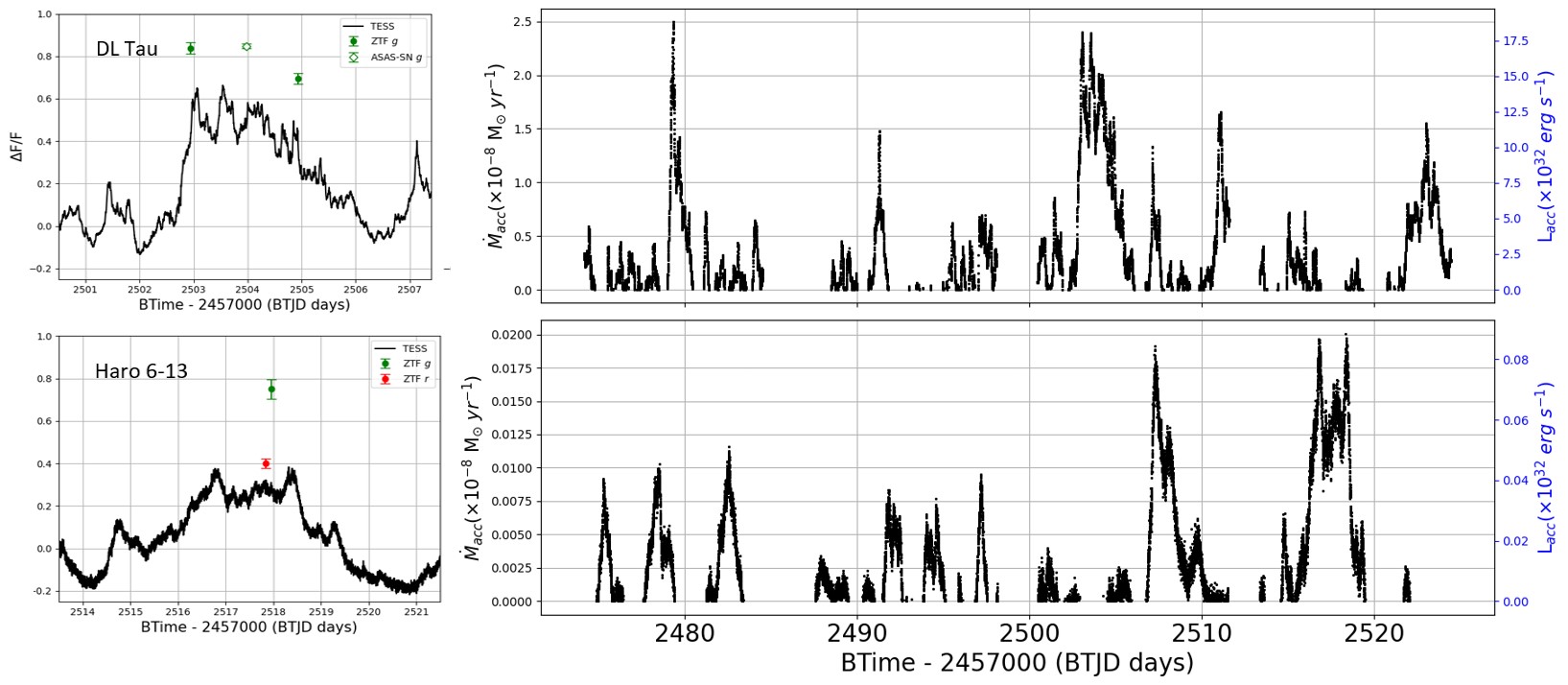
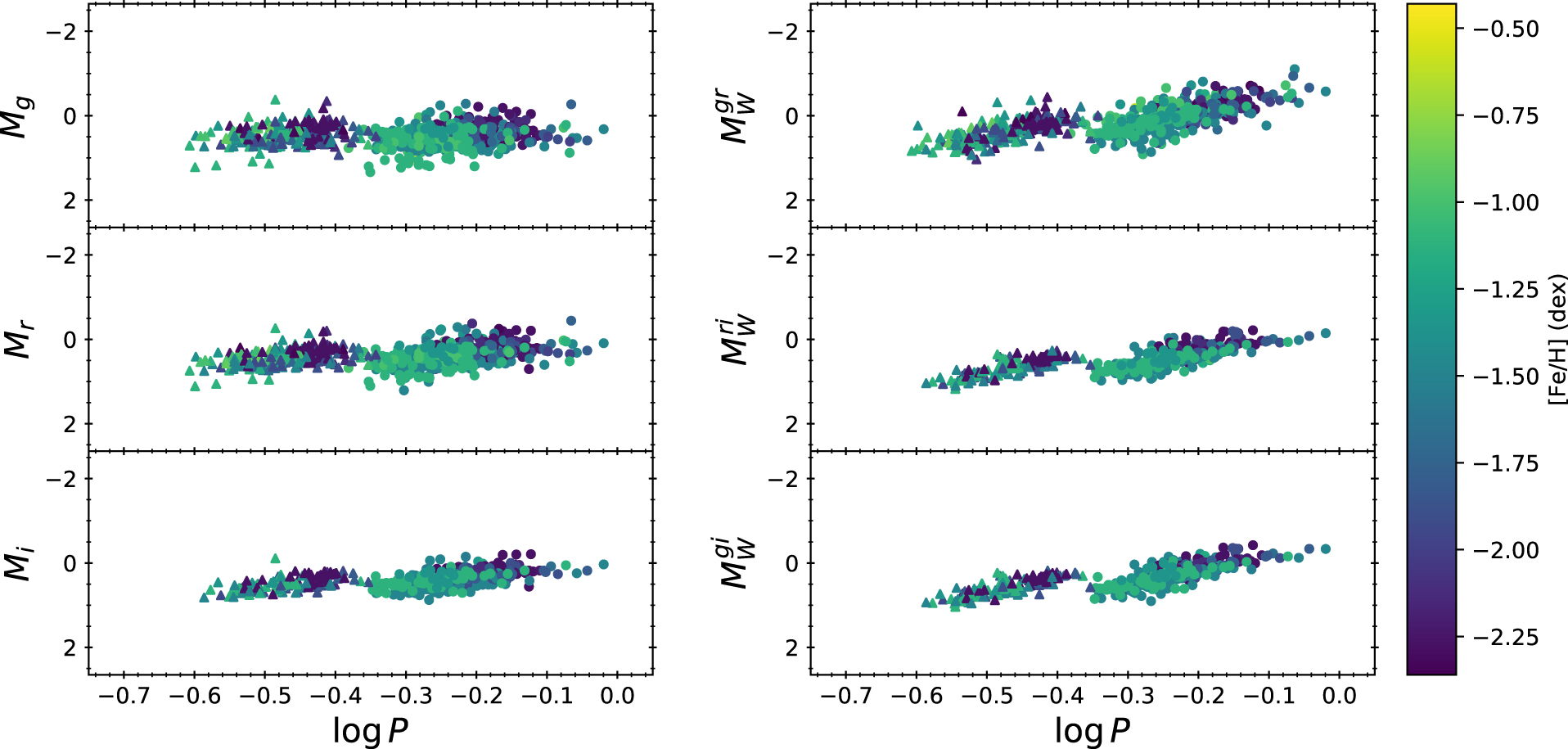
Caption: Temporal mass accretion rates during unstable accretion bursts. The upper panel shows DL Tau, and the lower panel shows Haro 6-13. The left side of the figure displays the simultaneous accretion luminosity bursts observed by TESS, ZTF, or ASAS-SN. The horizontal axis represents time (in days), and the vertical axis represents normalized flux. The right side of the figure presents the derived temporal mass accretion rates. The horizontal axis represents time (in days), and the left vertical axis (black) represents accretion rates (in units of M☉/yr), while the right vertical axis (blue) represents accretion luminosity (in units of erg/s).
PhD student Chia-Lung Lin: We have combined photometric and spectroscopic surveys from both space telescopes (TESS) and ground-based telescope (LAMOST, ZTF, and ASAS-SN) to study the mass accretion rates, flare activities, and variability characteristics of 16 Classical T Tauri Stars (CTTS) in Taurus. By calculating the flux of various spectral lines such as H-alpha, we derived an average mass accretion rate of 1.76×10-9 M☉/yr for these 16 CTTSs. Among them, two stars, DL Tau and Haro 6-13, exhibited temporary brightness increases in their TESS light curves due to bursts of unstable mass accretion rates. By analyzing simultaneous monitoring data from ZTF, ASAS-SN, and TESS, we estimated the time series variations in mass accretion rates for these two stars over a span of 50 days. If the results from spectral data reflect a stable accretion pattern, we concluded that the mass accretion behavior of these two stars is primarily driven by stable accretion. Additionally, we detected a total of 13 large flares across these 16 stars, with energy ranging from 2×1034 to 6×1035 erg, making their flare activity more than a hundred times more active than that of solar-like stars. We also found that the variability classes of these 16 stars change over time, with the timescales of these changes falling roughly between 1.6 to 4 years compared to results in the literature.
This study has been published in Astronomical Journal in 2023, August:
Lin, C.-L., Ip, W.-H., Hsiao, Y., et al. 2023, AJ, 166, 82 (Including Prof. Ip, Wing-Huen, master graduate Hsiao, Yao and Cheng, Tzu-Hueng in the IANCU)
DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/ace322
Show large images and more information










 Colloquium
Colloquium Journal Club
Journal Club
 鹿林天文台空拍
鹿林天文台空拍
 鹿林天文台一米望遠鏡
鹿林天文台一米望遠鏡
 一米望遠鏡控制室
一米望遠鏡控制室
 鹿林天文台一米望遠鏡
鹿林天文台一米望遠鏡
 中大天文台(科一館)
中大天文台(科一館)
 兩米望遠鏡
兩米望遠鏡

 Credit: LSST
Credit: LSST Credit: LSST
Credit: LSST